| 11 th Annual Pediatric Critical Care Colloquium |
| Session/Time | Cell Physiology/Sepsis/Sat, 8:00 - 9:30 AM |
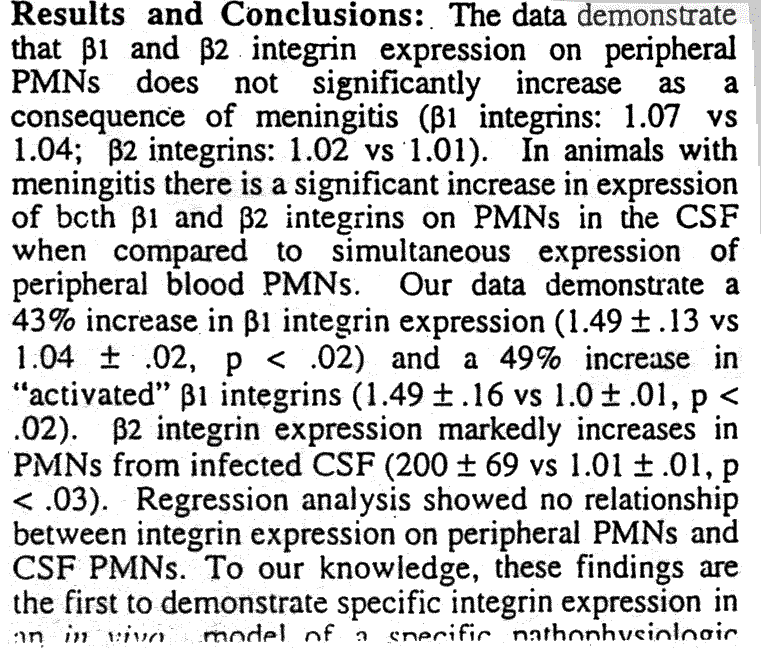
| Title | Integrin Expression on Neutrophils in a Rabbit Model of Group B Streptococcal Meningitis |
| Author | ME Rowin, R Pretzlaff, J. Frazuzta |
| Affiliation | Division ofpediatric Critical Care Medicine, Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH |
| Introduction | The consequences ot neurropnii (PNDN) migration in meningitis are well known. Products released by PMNs are injurious to the endothelium and result in alterations of the blood brain barrier. Integrins are cell surface heterodimers that play a pivotal role in inflammation by allowing PMNs to adhere to the endothelium and n- grate through the extracellular matrix. We examined the expression of pi and P2 integrins on PMNs from blood and CSF in an animal model of meningitis. |
| Method | New Zealand' AUte rabbits (n = 6) were anesthetized and blood was obtained to establish baseline expression of pi and p2 integrins on peripheral PMNS. The cistema magnae was punctured and 0.4 n-A of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) was obtained. The animal were then inoculated intracistemadly with 0.4 n-d of a saline solution containing I X 10' cfu/mi of group B streptococcus. The rabbits were allowed to recover with free access to food and water. Eiaht hours post-inoculation the rabbits were treated with Ceftriaxone (50 mg/kg) and a subcutaneous bolus of 120 cc's normal saline. At 24 hours post-inoculation, a second cistemal tap was performed and I ml of CSF was removed. Blood was obtained for concurrent integrin analysis. Using flow cytometry, we analyzed the expression of Pi and P2 integrins on PMNs from both blood and CSF. |

Use your browser's back button to return to the appropriate index of abstracts...
Back to PCCC 98 Abstract Introduction | Back to PCCC 1998