| 11 th Annual Pediatric Critical Care Colloquium |
| Session/Time | Poster/Thu, 4:30 - 6:30 PM |
| Title | Substrate Oxidation in Critically III Children |
| Author | JA Coss-Bu, MD; WJ Klish, MD; D Waiding, BSBE; Y David, PhD; E O'Brian Smith, PhD; LS Jefferson, MD |
| Affiliation | Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX |
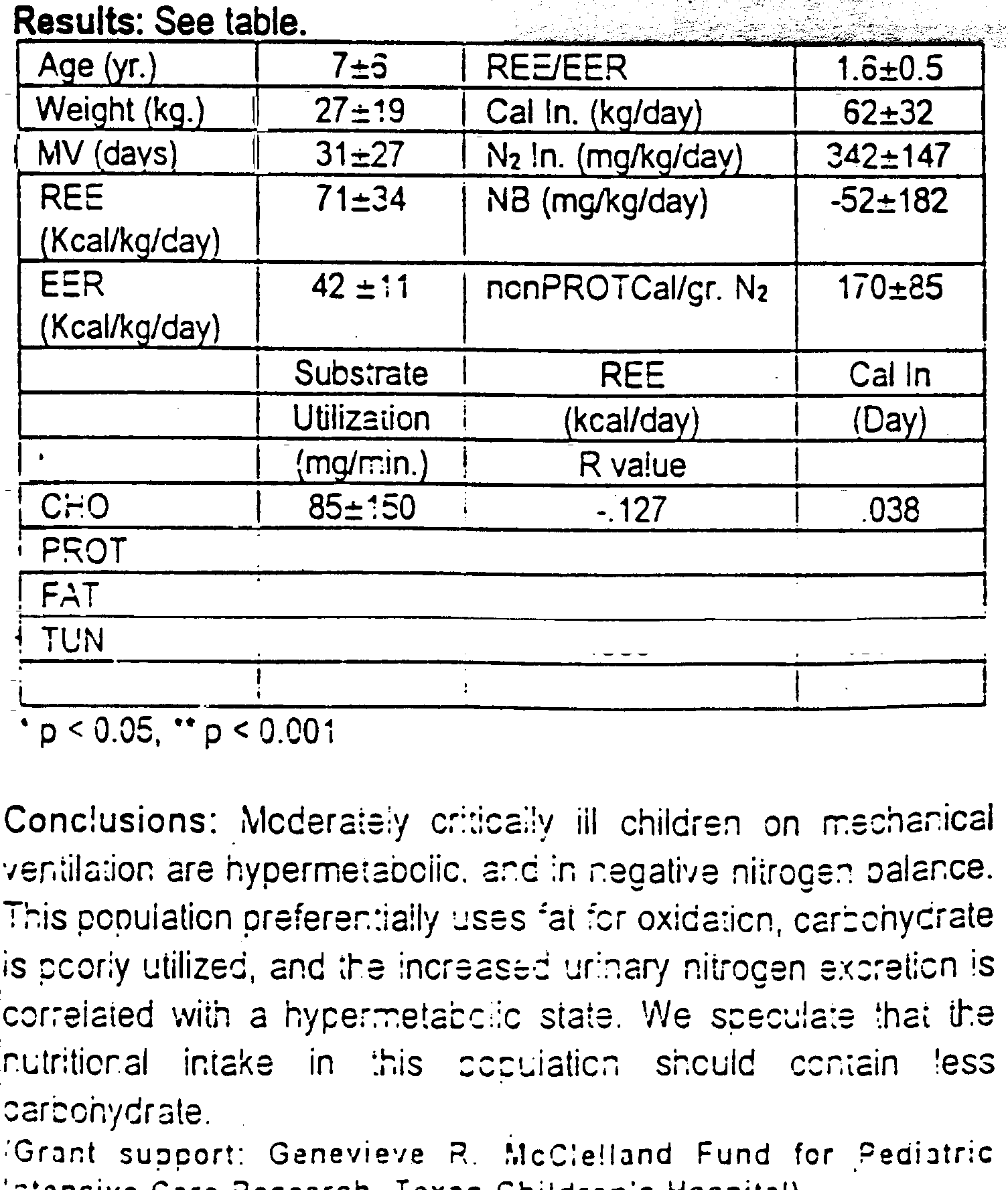
| Introduction | Critically ill patents usually are catabolic, as assessed by nitrogen balance (NS) studies. Whei indirect calorimetry (IC) and total urinary nitrogen (TUN) are done simultaneously; carbohydrate (CHO), protein (PROT), and fat ufilization can be calculated. |
| Method | This study measured NS and substrate ufilizadon in 20 critically ill children (mean FIRISM and TISS scores of 8±5 and 30+:7 respectively) on mechanical venfiladon (MV), in relation to their resfing energy expenditure (REE) and caloric intake (Cal In.) AJI patents were receiving TPN or enteral nutrifion when evaluated. REE was measured by IC (mass spectrometry) and TUN by the Kieldahl method. Expected energy requirements (EER) were obtained from Talbot's tables. REE/EER index > 1.1 defined a hypermetabolic state. Substrate utilization rates were calculated using the Consolzio formulas. Studies were done at the fime of the first evaluation and repeated (n=48). The correlation was measured by Pearson's coefficient. Values are mean + SD |
| Result |  |
Use your browser's back button to return to the appropriate index of abstracts...
Back to PCCC 98 Abstract Introduction | Back to PCCC 1998