| 11 th Annual Pediatric Critical Care Colloquium |
| Session/Time | Poster/Thu, 4:30 - 6:30 PM |
| Title | An In Vivo Model of Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury |
| Author | LJ Heman, MD; MS Dowhy; AT Rotta, MD |
| Affiliation | State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, New York |
| Introduction | A porcine model that allows independent ventilation and perfusion of right and left lungs was used to describe effects of in situ, nonhypoxic pulmonary ischemic- reperfusion injury. |
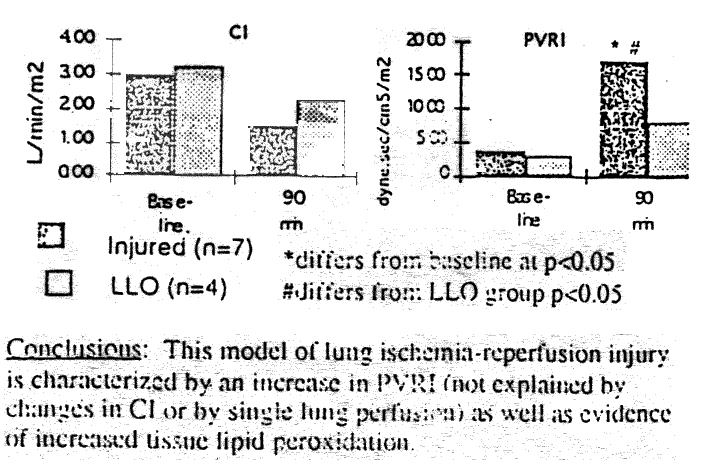
| Method | Piglets were anesthetized and instrumented. Aortic, right atrial, and pulmonary artery catheters were placed. A double lumen endotracbeal tube was placed through a tracheostomy. Animals were ventilated in a pressure control mode with an FiO2 of I.O. A left thoracotomy incision allowed access to the left bronchus, and right and left pulmonary arteries. ne bronchial circulation to the left luna was occluded. Vascular snares were placed around the right and left pulmonary arteries. A left atrial line was placed. Animals were allowed to recover. Left lung iscbemia was induced by occluding the left pulmonary artery for I hour. Cardiac output was directed to the right lung through the right pulmonary artery. Respiratory rate was increased to maintain baseline minute ventilation, and only the right funa was ventilated. The left luna was reperfused by unclampina the left pulmonary a elartery while clamping the right pulmonary artery. During the 2 hour reperfusion period, only the left lung was ventilated. Measurements of gas exchange, fiemodynamics, and pulmonary mechanics were made. The surviving animals were sacrificed after 2 hours of reperfusion. The lunos were removv for measurement of malondialdehyde (iADA), a marker of lipid peroxidation. 'nree groups were studied: an injured group (n -7) that underwent left lun- iscbemia and reperfusion; a group who was supported for 2 hours on their left lung only (LLO) without prior ischen-da (n=4) to determine the effects of 2 hours of single lung perfusion, and a sham-operated control. group that underwent the surgical procedures but was supported on both luncs for the 3 hour study period. Data are reported as means. Significant statistical differences were defined as p<0.05. < 0.05 |
| Result | The sham operated control aniin s did not chanoe over time. Three of the 7 injured animals died after 90 minutes of reperfusion. Median MDA was greater in the injured left lungs (250 nanonioleslaram luna tissue) than in the LLO luncs (87 nanomoleslgmm luno tissue) or in lungs of sham-operated controls (62 nanomoles/oram IuQo tissuc). |
| Conclusion |  |
Use your browser's back button to return to the appropriate index of abstracts...
Back to PCCC 98 Abstract Introduction | Back to PCCC 1998