| 11 th Annual Pediatric Critical Care Colloquium |
| Session/Time | Pulmonary II/Thu, 2:00 - 4: 00 PM |
| Title | Is Improved Oxygenation A Valid Indicator of Responsiveness To Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Patients with Severe Ards? |
| Author | M Baidauf, P Silver, C Rosenthal, M Sagy |
| Affiliation | Schneider Children's Hospital, New Hyde Park, New York |
| Introduction | Changes in patients' oxygenation index, position (supine vs. prone), blood Peo, values, blood pH values and dosages of vasoactive drugs can all affect oxygenation during .management of severe ARDS. When some or all of these changes occur amid iNG treatmen the validity and specificity of improved oxygenation as a response to iNO is uncertain. : To test the hypothesis that in patients with severe ARDS, fluctuations in the aforementioned variables occur frequently and therefore improvement in oxygenation during 1NO may be erroneously attributed to iNO effect. |
| Method | Sixteen patients were
treated with 1NO for pulmonary Hypertension. Six of these patients met our definition of
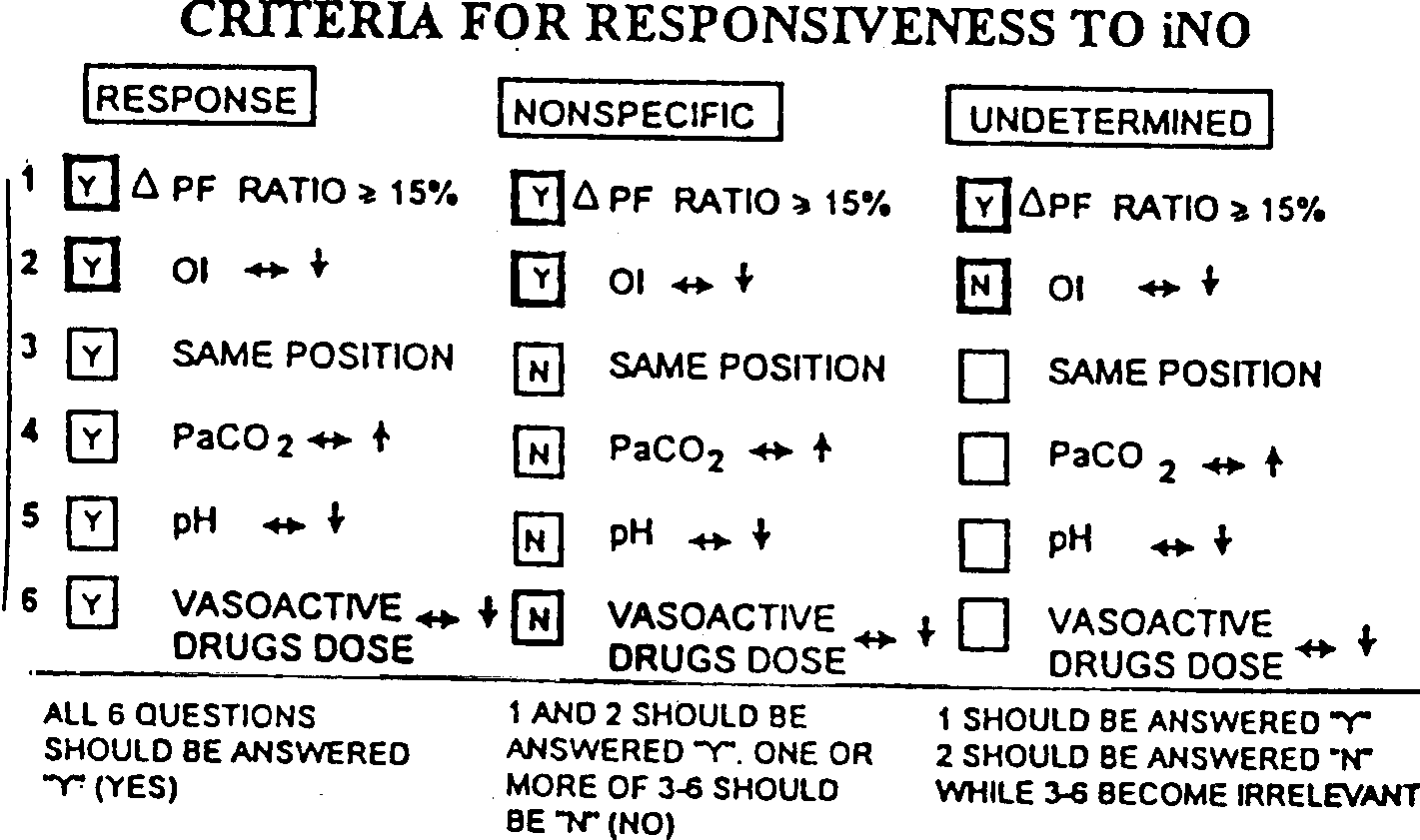
,severe ARDS (PaO FiO, <1 I 0 and 01> 1 9 prior to iNO initiation). 'We developed a post hoc analysis
tool which included 6 criteria (figure).to determine whether or not an observed
improvement in oxygenation can be attributed solely to iNO. We evaluated data points at
predetermined intervals of iNO treatment during the first 72 hours.
|
| Result | The PaO,/Flo, prior to initiation of iNO was 85 +17 (range: 62-105) and the Of was 31+ 9 (range 20-45). iNO doses ranged from 5 to 25 ppm. Four patients were treated with conventional mechanical ventilation and 2 %vith high frequency oscillatory vc!itilation. A total of 37 data poins kvcrc Evaluated Nvithin a 72 hotir period of 1NO treatment. In twelve data points (32%) the PnO,/FiO, Nvas less than 141"% of the pre-iNO b -seline value and thus did not meet the response criterion. In 10 data points (27%) the observed response %vas nonspecific, as other en'teria specified in otirinaivsls tool for "nonspecific response" Nvere not met. In I data noint (3%) the observed improvement in o.\vgenation ,;ould not be :ittribtited to iNO (undetennlvcd), as an iiicreaic III 01 vas also documented. fii fourteen data points (33%) the increased I"iiO,i'riO, ratio could be ittribLIted to the iNO treatment as no other conti-lbtitoi-y factors vei-c Identified |
| Conclusion | In severe ARDS improvement in oxygenation amid iNO treatment is mulfactorial. Only in 38% of our evaluated data points the increase in PaO2/FiO2 could be attributed to iNO. We suggest that in future iNO studies, our described additoinal criteria. |
Use your browser's back button to return to the appropriate index of abstracts...
Back to PCCC 98 Abstract Introduction | Back to PCCC 1998