| 11 Th. Annual Pediatric Critical Care Colloquium |
| Session/Time | Pulmonary I/Thu, 9:45 - 12 00 PM |
| Title | Selection of an Appropriate Level of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Using Alveolar Dead Space Volume |
| Author | HK Spalding, MD; MJ Banner, PhD; M Sungar, MD; JW Skimming, MD |
| Affiliation | University of Florida College of Medicine, Depts of anesthesiol, Pediatr, and Physiol, Gainesville, Florida |
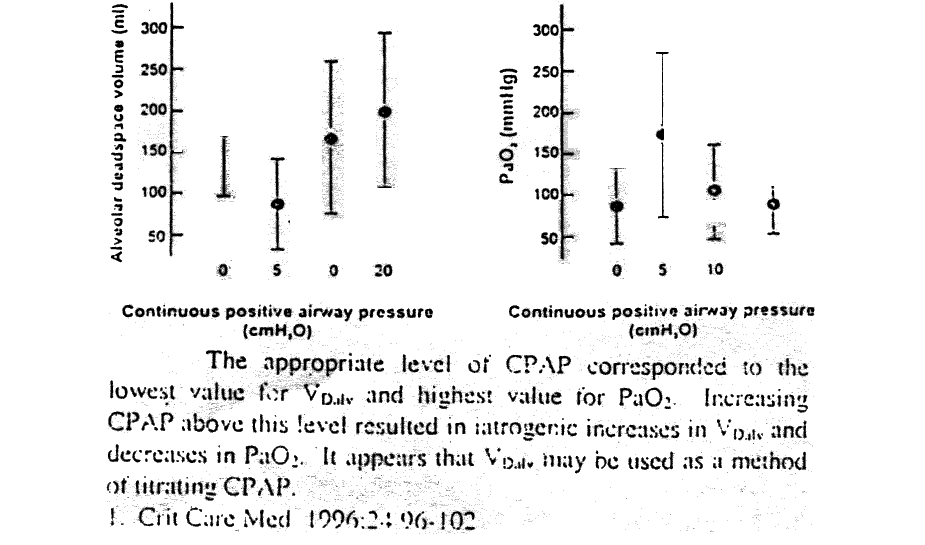
| Introduction | CPAP administered to pa6ents with acute lung injury is known to increase functional residual capacity, decrease intrapulmonary physiologic shunt, and improve arterial partial pressure of oxyogen (PaO2). The optimum CPAP is usually determined by the level that maximizes PaO2 without compromising, hemodynarics or increasing alveolar dead space volume (Vdalv). The latter is the result of over distending compliant alveoli converting zone 2 and 3 alveolar units into zone I units. The purpose of the study was to deternine if Vdlv, could be used to select an appropriate level of C AP in subjects with acute lung injury. |
| Method | After approval from the institutional animal care and use committee, 6 sheep (66.33 ± 6.47 k.a) were anesthetized with an infusion of sodium thiopental; intermittent injections of pancuronium were used for muscle relaxation. A thermodilution pulmonary artery catheter and arterial catheter were inserted. The animals were intubated (8.0-mm endotracheal tube) and connected to a ventilator (Bear 1000) with an FiO2 of I.O. Data from a flow sensor and an infrared capnometer, positioned between the Y piece of the breathing circuit and the endolracheal tube, were directed to a commercially available respiratory monitor (Novametrix Medical Systems), which calculated Vt)m, usina the sincle breath C02 technique (1). Hydrochloric acid (pH 2.5, 0.25 was instilled intratracheally to induce acute luna injury.Each sheep received CPAP of 0, 5, 10, and 20 cm HzO in random order. Data were analyzed using a repeated measures ANOVA; alpha was set at 0.05 for statistical significance. |
| Result | Following lung injury,Vdalv increased and PaO2 de- creased sianificantly with a CPAP of 0 cm H2O. Vdalv decreased and PaO-2 increased sicnilicantly with a CPAP of 5 cm H20. Vdalv increased sianificanti and PaO7. decreased significantly with a CPAP of 10 and 20 cm H2O when compared to 5 cm H2O CPAP |
| Conclusion |  |
Use your browser's back button to return to the appropriate index of abstracts...
Back to PCCC 98 Abstract Introduction | Back to PCCC 1998
Use your browser's back button to return to the appropriate index of abstracts...
Back to PCCC 98 Abstract Introduction | Back to PCCC 1998